News
Prevent Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)—especially syphilis and chlamydia—are on the rise in Colorado. While there have been advances in the treatment of STDs, it continues to be true that “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.”
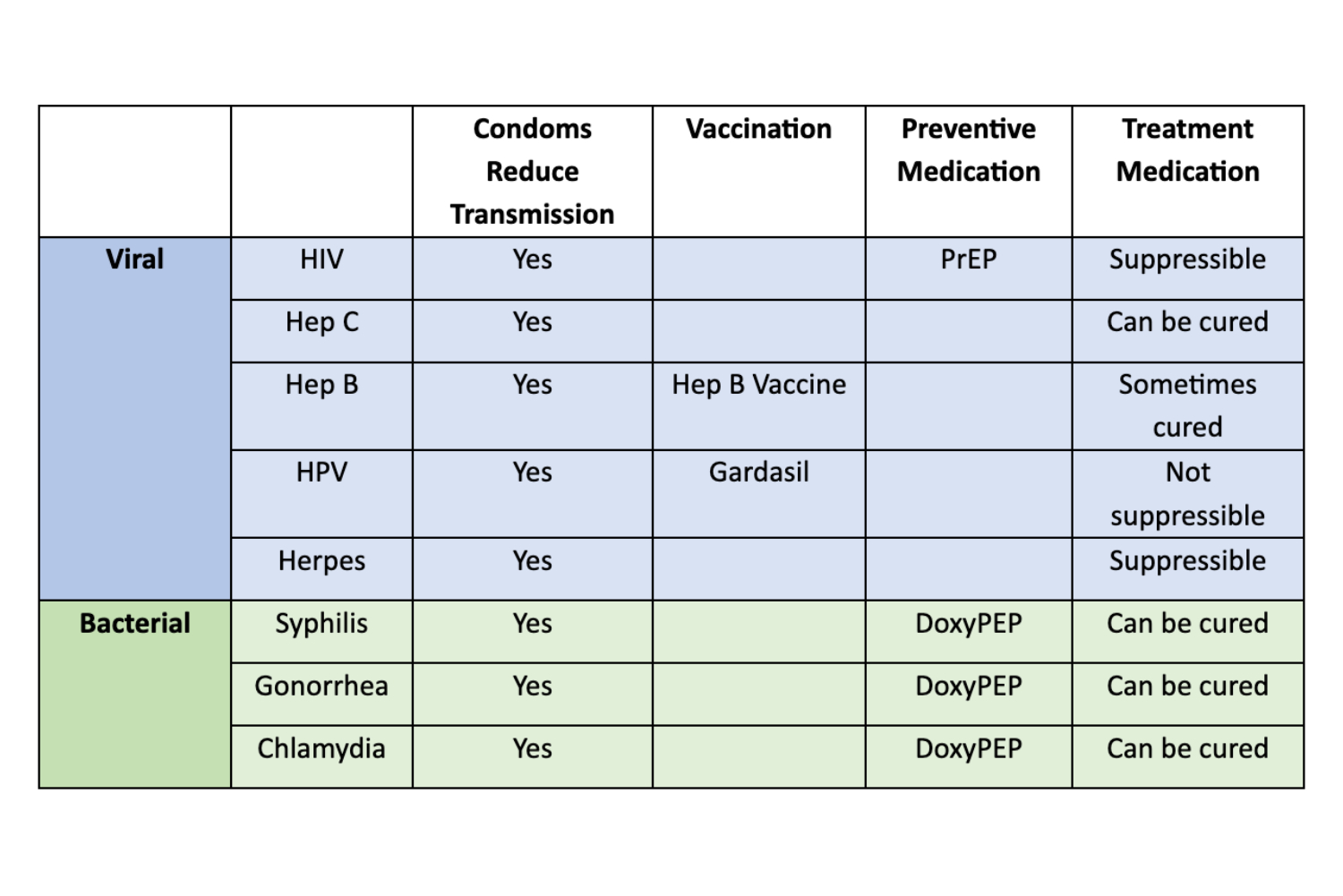
There are a number of ways to prevent and treat STDs, including condoms and dental dams, vaccinations, preventive medications and treatment medications. Abstinence is the highest form of prevention, but monogamy (sex with only one partner who has been tested and does not have a sexually transmitted infection) can also reduce the risk of contracting an STD. That said, patients should never feel embarrassed or judged when discussing their sexual history. There are a number of strategies that can make sex safer. The following chart can be helpful in understanding the prevention and treatment of a variety of both viral and bacterial sexually transmitted diseases.
What is the HepB Vaccine?
HepB, or the hepatitis B vaccine, is a series of shots that protects against hepatitis B, a liver infection that can lead to chronic liver failure and liver cancer. Hepatitis B is spread through blood, semen or other body fluid infected with the hepatitis B virus. People can become infected through birth (if a woman has hepatitis B, her baby can become infected); sharing items such as razors or toothbrushes with an infected person; contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person; sex with an infected partner; sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injectables; or exposure to blood from needlesticks or other sharp instruments. Because there are so many ways a person can become infected, the Centers for Disease Control recommends the HepB vaccine for all ages.What is Gardasil?
Gardasil is a vaccine that protects against nine types of the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is extremely common–over 90% of men and 80% of women will contract it in their lifetime. Most people clear HPV on their own, but certain strains can stick around and cause cervical, rectal or throat cancer. Because HPV is so common, vaccination is most effective before a person becomes sexually active. The Gardasil vaccine is a set of two shots for boys and girls ages 9-15, or a series of three shots for anyone after the age of 15. The vaccine is FDA-approved up to age 45, but most insurances will only cover it to age 27. Some patients may elect to get the vaccine even after the age of 27 if their life situation changes, if they have an abnormal pap smear, or if they want to be proactive about avoiding high risk strains for HPV.What is PrEP?
“PrEP” stands for pre-exposure prophylaxis. It refers to a preventive medication that is used to prevent contracting HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. The most common brands are Truvada or Descovy. This is a pill that is taken daily. PrEP is effective in both men and women, regardless of who their sexual partner may be. The CDC recommends PrEP for anyone who has had vaginal or anal sex, who is not consistent with condom use, or who has had been diagnosed with an STD in the last six months. Patients should receive regular testing while they are on this medication; usually every three months. Colorado Mountain Medical can perform testing, as can Rocky Mountain Planned Parenthood in Glenwood Springs. Most reputable online sites, like Mistr, also offer regular testing.What is DoxyPEP?
“DoxyPep” is post-exposure prophylaxis used to prevent bacterial infections such as syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia. DoxyPep is recommended for men who have sex with men and transgender women. It is not currently recommended for cisgendered women because some studies have suggested that it might not be as effective in this population. Doxycycline is an antibiotic. Two pills are taken after unprotected sex to prevent infection. I teach patients the 3:2:1 mnemonic for DoxyPEP: take the medication within 3 days of unprotected sex, take 2 tablets, and only take it once in a 24hr period. Folks on DoxyPEP should also receive regular testing.Do I need both PrEP and DoxyPEP?
There is a lot of overlap in the populations who could benefit from each of these preventive strategies. PrEP and DoxyPEP can be taken together; they don’t interact with each other. Your primary care provider can help you decide if you need one or both of these medications.Who Should I Talk to About My Sexual Health?
It’s always important to remember that prevention, regular testing and early treatment can help stop the spread of sexually transmitted diseases. Talk to your primary care provider about your sexual history and STD testing. Colorado Mountain Medical’s primary care team can guide you through testing, diagnosis and treatment.More News
-
More

The Benefit of Doing Hard Things
How Creating Resiliency Impacts Long-Term Health I had just returned from my first Hyrox, a fitness race...
-
More

Spring Is in the Air, And So Are Allergens—How to Combat Spring Allergies
For some of us, April marks the end of the ski season. For allergy specialists like me, it means the beginning of a...
-
More
The 3 Cs of Measles
Recent news reports on measles outbreaks have brought the once-dormant disease to the forefront of many...





